CS101 算法与数据结构
有序数列的存储
-
List ADT
一个序列, 不是列表. 有序.
- 操作: CURD 增删改查, 可以找到当前点的前后, 获取长度, 是否为空
-
array
这是一个正常见到的一个数组.
增删不容易做(把后面的向后或向前整体移动,
O(n)), 但是改查是容易的(地址直接查O(1)) -
链表
指针指向下一个
快速增删, 查找复杂
class List; class Node { private: int data; Node * next_node; public: int retrieve() const { return data; } Node * next() const { return next_node; } friend class List; } class underflow {} class List { private: Node *list_head; public: List() { list_head = nullptr; } ~List() { while (list_head) { pop_front(); } } // Accessors bool empty() const { return !list_head; } int size() const { int cnt = 0; for (Node * ptr = list_head; ptr != nullptr; ptr = ptr->next()) { cnt++; } return cnt; } int front() const { if (empty()) { throw underflow(); } return list_head->retrieve(); } Node *head() const { return list_head; } int count(int elem) const { int cnt = 0; for (Node * ptr = list_head; ptr != nullptr; ptr = ptr->next()) { if (ptr->retrieve() == elem) cnt++; } return cnt; } // Mutators void push_front(int elem) { list_head = new Node( n, list_head )} int pop_front() { if (empty()) { throw underflow(); } int ret = front(); Node * head_ptr = list_head; list_head = list_head->next(); delete head_ptr; return ret; } int erase(int elem) { int cnt = 0; for (Node * ptr = list_head; ptr != nullptr; ptr = ptr->next()) { if (ptr->next() && ptr->next()->retrieve() == elem) { Node * next = ptr->next(); ptr->next_node = next->next(); delete next; cnt++; } } return cnt; } }; -
双向链表
两个指针, 一个指向上一个, 一个指向下一个
-
用数组模拟链表
可以用两个数组, 一个存
data, 一个存data的next_index开空间同
vector, 开双倍空间, 但是空间可能浪费优势:
new的次数少.new是底层操作, 很耗时
时间复杂度
一般来讲, 指的是worst case的时间复杂度.
二分查找: average:
: . 那么就有时间复杂度为
: , 有
| 时间复杂度 | 极限式 |
|---|---|
HashTable
将Object映射到一个数字,然后将数字映射到一个地址(内存空间)
有大小的空间,个要存入的物体,冲突的概率为
hash函数
必要:
- hash值必须是可以确定的(两次对同一个Object进行hash得到相同的值)
- 相同的Object必须有相同的hash()
最优:
- 必须很快:
- 如果两个物体是随机抽取的,那么两个物体应该等可能的分布在0-m的范围里。(是的概率相同)
Predetermined
class HashPredetermined {
public:
HashPredetermined(){
hashValue = hashCount;
hashCount++;
}
unsigned int hash() const {
return hashValue;
}
private:
unsigned int hashValue;
static unsigned int hashCount;
}字符串hash
对于字符串,可以直接计算他们的char的值:
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
hash += str[i];
}但是是一个的算法。
优化:只取其中一部分:
for (int i = 0; i <str.length(); i *= 2){
hash += str[i];
}存地址:
取最后三位,然后转成10进制存到长度为8的数组中,然后遍历寻找:
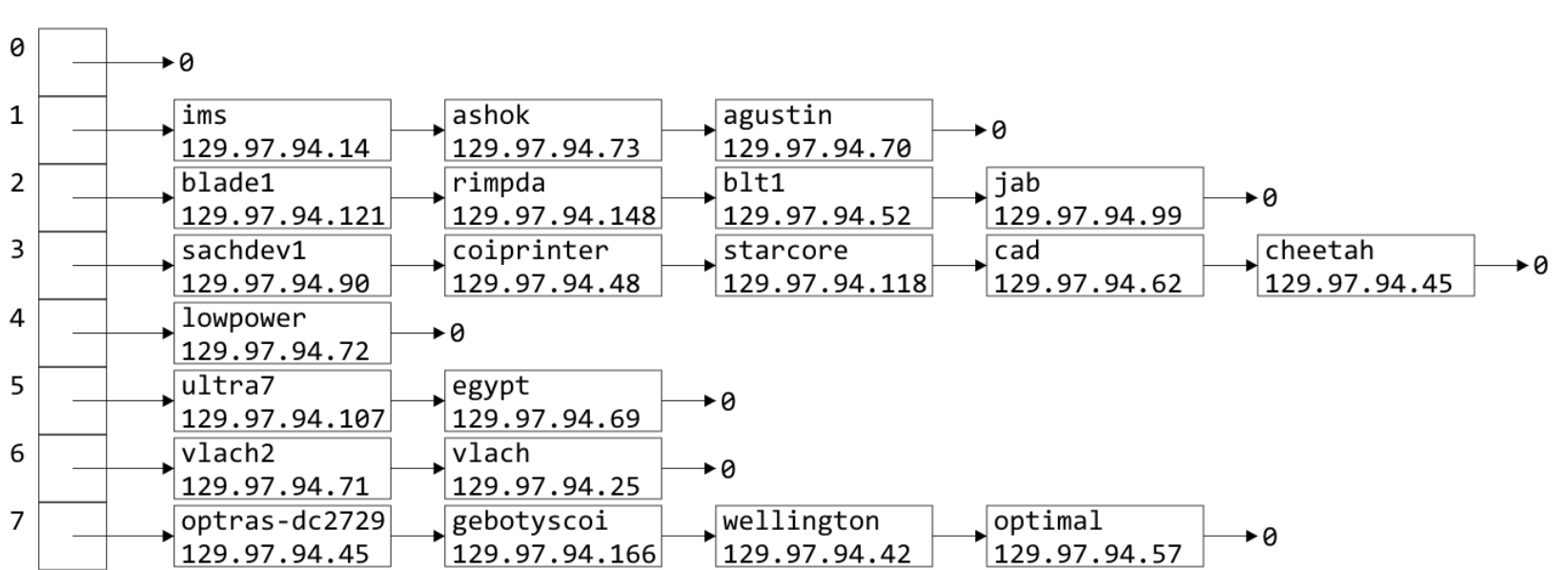
设n个物体,M的内存空间,令叫做load factor。表示每次寻找平均需要找多少个物体。那么空间复杂度就是
比特运算
取其中一部分(2进制最后的一定的数字转成10进制)
unsigned int C = 581869333;
unsigned int hash_M( unsigned int n, unsigned int m ) {
unsigned int shift = (32 – m)/2;
return ((C*n) >> shift) & ((1 << m) – 1);
}排序
- 稳定的算法:处理两个相同的元素的时候不会交换这些元素
插入
稳定的
冒泡
稳定的
归并
快速
纠正逆序对的方法。速度更快就是纠正逆序对的效率高,一次操作纠正很多逆序对
最坏复杂度:
最优复杂度:
平均复杂度:
递归调用
worse case: 总是选左边的,导致左边的永远没法分割,需要遍历整个数组而非递归
Master Theorem:
数据结构
略